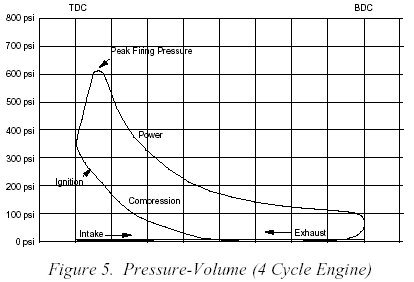
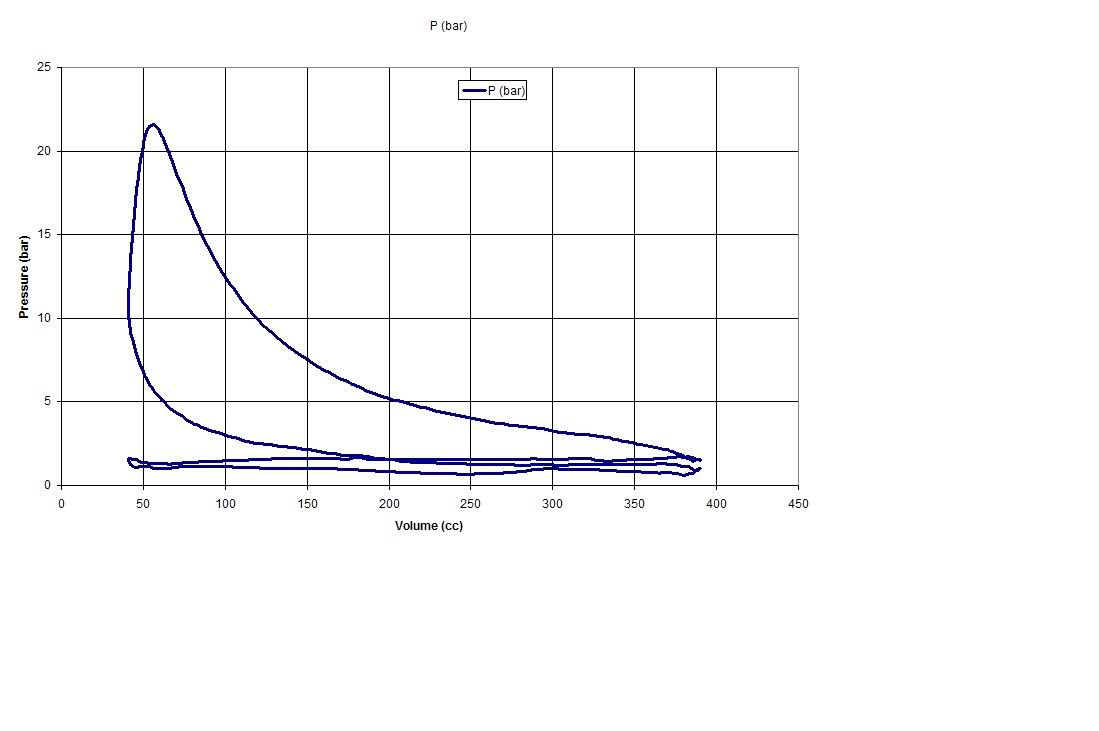
I got asked how to select the correct cylinder heads, and in respect to a 383 a guy was building, now that may seem like an easy question but the truth is that without knowing the intended cam, compression, rear gear ratio and intended power range,
thats about as easily answered as asking which girl will make the best wife!
yeah we have all heard some guys discussing which cylinder heads and theres always some guy that says that head (A) or (B) has intake ports that are too large or too small, and many guys never stop to ask WHY?... WHY? that particular cylinder heads to much larger or too small and how can you even tell? in fact how many guys can even tell you the measured difference in cross sectional area or that heads flow numbers?
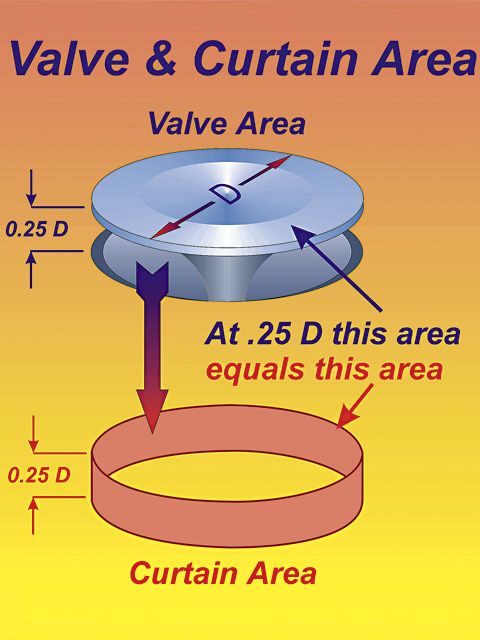
well, lets look at the basics, all cylinder head flow is controlled by several factors,port flow is restricted by the smallest cross sectional area of a port, the valve curtain area, and the valve seat throat, but one basic restriction is valve size and how high the valves lifted off it seat (cam lift)and how long it remains open, (cam duration) this is the valve curtain area all ports must deal with,and Ive heard guys state that the higher the lift the more the port will flow,well the cam timing and compression all effect your potential results.
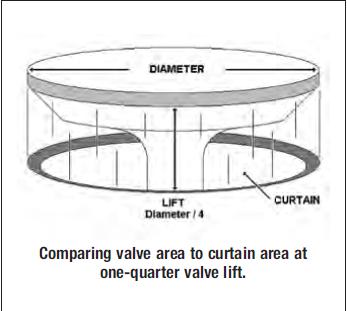
well lets put that myth to bed first, a port throat area rarely exceeds .90% of the valves diameter., and no matter how high the valve lifts off its seat the flow can not increase too significantly much greater that the flow reached when that valve curtain area equals the port throat cross sectional area, as the smaller forms a restriction to the other.
on some heads and intake manifolds the port cross sectional area is significantly smaller than the valve curtain,
http://www.airflowresearch.com/super-chevy-apr-2010-210cc-sbc.php
EXAMPLE
this is one reason the TPI intake is rather restrictive
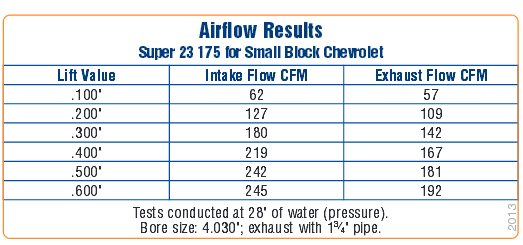
http://www.wallaceracing.com/chokepoint-rpm.php
heres a typical flw vs lift graph, notice how the flow rate increases past .500 lift drop rather drastically

now holding the valve open longer allows more flow just like opening a door fully allows easier access to a room but at some point just like a door opening limits the number of people that can enter a room per second so does the port throat, curtain area and any restriction in the port.
lets take your common 2.02 small block chevy intake valve, its surface area is 3.21 square inches but the port throat restriction would be exceptionally good if it was at ,90% or 2.89 square inches, a 2.02 valve has a circumference of about 6.3 inches so at about .47 inches of lift port flow increases with further lift starts to drop off
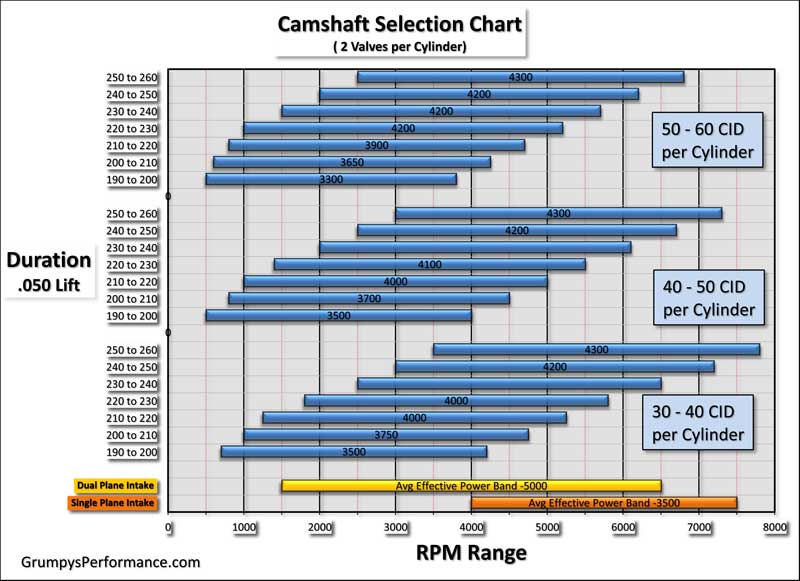
you will want to match the cam timing to the intended power range, and match the engine static compression ratio to the cam timing to get a dynamic compression ratio that will work without getting into detonation issues with available fuel octane levels.
(READ THRU THESE LINKS)
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=82
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=5078
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=796
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=727
IF YOU HAVE A SET OF REALLY DEEP POCKETS
http://www.speierracingheads.com/SRH2.50.htm
CALCULATORS
http://www.wallaceracing.com/calcafhp.php
http://www.wallaceracing.com/calchpaf.php
http://www.rbracing-rsr.com/runnertorquecalc.html
http://horsepowercalculators.net/intake ... old-design
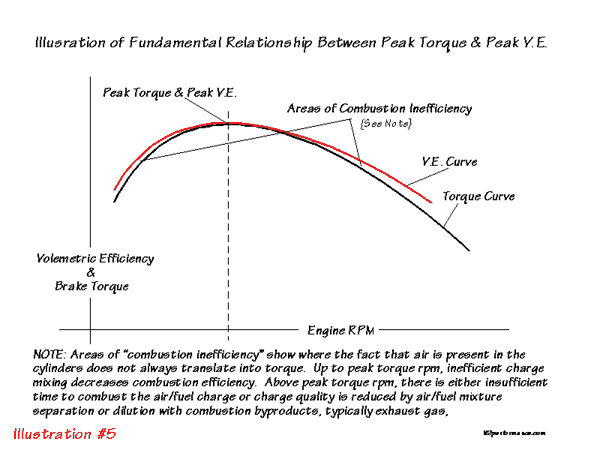
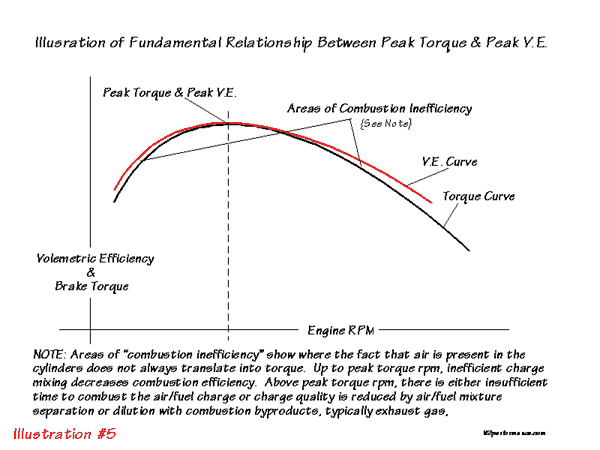
power generated by an engine is closely linked to how efficiently it makes torque, in a given rpm range and how fast the engine can be rotated to increase the number of EFFECTIVE power strokes per second, so it should be obvious that the larger the displacement the more fuel/air mix can be burnt and the faster each cylinder can be filled and fired and scavenged and recharged the more power can potentially be produced. smaller ports will have higher flow velocity's making them more effective at filling cylinders at lower rpms but restricting upper rpm power.
larger ports tend to be far less restrictive to flow but also tend to have slower response in the lower rpm ranges
as the engines ability to efficiently fill and scavenge the cylinders is based on both port flow and time available for that port flow as the engines rpm rate increases the efficiency increases with the air flow rate inertia in the runners and ports up to the point where time limits the ability for the ports to fill, fire and scavenge efficiently, thats why you torque curve and volumetric efficiency are so closely linked.
http://www.summitracing.com/parts/tfs-3 ... /overview/
http://www.summitracing.com/parts/tfs-3 ... structions
you are aware theres reasonably priced aluminum heads designed for a small bore sbc that out flow standard vortec heads
heres a few serious sbc heads
http://www.profilerperformance.com/sbc-heads-176.html
http://www.airflowresearch.com/index.php?cPath=24_33

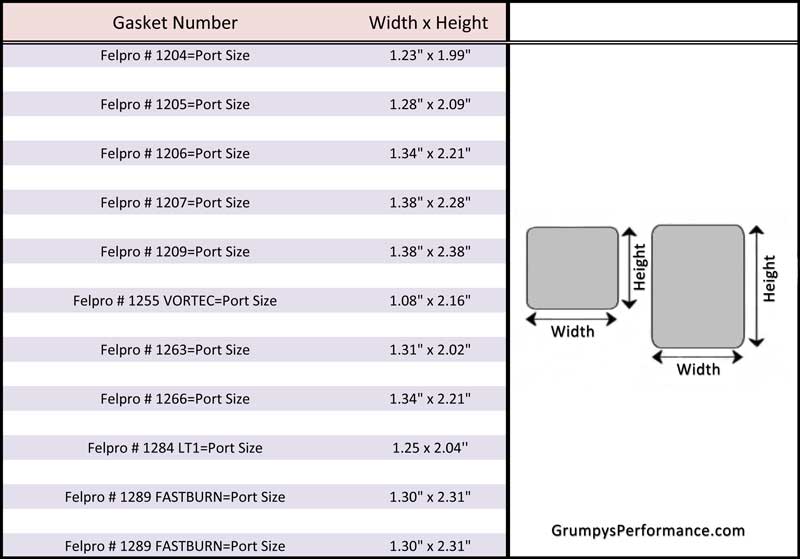
here’s a chart FROM THE BOOK,HOW TO BUILD BIG-INCH CHEVY SMALL BLOCKS with some common cross sectional port sizes
(measured at the smallest part of the ports)
...........................sq inches........port cc
edelbrock performer rpm ....1.43.............170
vortec......................1.66.............170
tfs195......................1.93.............195
afr 180.....................1.93.............180
afr 195.....................1.98.............195
afr 210.....................2.05.............210
dart pro 200................2.06.............200
dart pro 215................2.14.............215
brodix track 1 .............2.30.............221
dart pro 1 230..............2.40.............230
edelbrock 23 high port .....2.53.............238
edelbrock 18 deg............2.71.............266
tfs 18 deg..................2.80.............250
you don,t generally find a ports most restrictive or smallest cross section at the intake to head gasket match so measuring a port at that point is usually nearly meaningless.
notice how the port cc range does NOT exactly reflect the cross sectional areas
also notice how the 210cc AFR port is only about 4% larger in cross sectional area, a change in area that will cause about a 150rpm change in the ports low rpm torque peak , but the increased flow will have a much more significant effect on the engines power, while its true that the smaller port will make a bit more low speed torque its also true that its smaller cross section is far more restrictive to upper rpm peak hp than the slightly larger port and its the, engine displacement, compression ratio, ignition timing curve, cam timing and intake runner and plenum, header length, collector design and and exhaust back pressure, selected that have by far the larger effect on the engines power curve in the low and mid rpm ranges
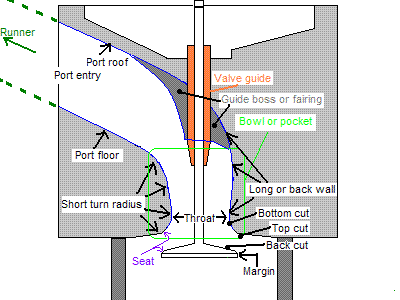
you will usually need snap gauges and a micrometer to measure the port throat and the area near the push rod passage where many ports tend to be pinched tighter
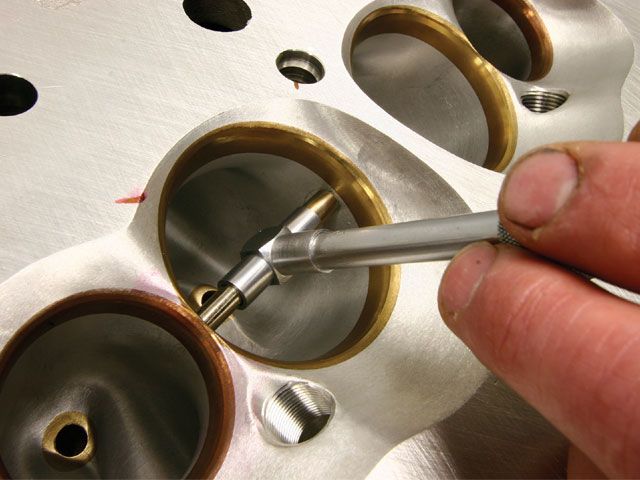



there are very useful calculators to use to calculate the ideal port cross sectional area, and to use to find when a ports to small and restrictive or two large and sluggish, but it requires measuring the ports to get the correct info
http://www.rbracing-rsr.com/runnertorquecalc.html
http://www.wallaceracing.com/max-rpm2.php
http://www.wallaceracing.com/max-rpm.php
http://www.wallaceracing.com/ca-calc.php
http://www.wallaceracing.com/chokepoint-rpm.php
http://www.wallaceracing.com/area-under-curve.php
http://www.wallaceracing.com/curtain-area-calc.php
http://2.3liter.com/Calc2.htm#MinCross
related useful threads, with a ton of related info that will help in any head selection
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=333
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=796
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=148
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=2630
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=266&p=322&hilit=215cc+vortec#p322
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=4664
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=4081
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=1563
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=4221
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=401
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=92
viewtopic.php?f=55&t=1038\
viewtopic.php?f=55&t=5378
viewtopic.php?f=55&t=4362
thats about as easily answered as asking which girl will make the best wife!
yeah we have all heard some guys discussing which cylinder heads and theres always some guy that says that head (A) or (B) has intake ports that are too large or too small, and many guys never stop to ask WHY?... WHY? that particular cylinder heads to much larger or too small and how can you even tell? in fact how many guys can even tell you the measured difference in cross sectional area or that heads flow numbers?
well, lets look at the basics, all cylinder head flow is controlled by several factors,port flow is restricted by the smallest cross sectional area of a port, the valve curtain area, and the valve seat throat, but one basic restriction is valve size and how high the valves lifted off it seat (cam lift)and how long it remains open, (cam duration) this is the valve curtain area all ports must deal with,and Ive heard guys state that the higher the lift the more the port will flow,well the cam timing and compression all effect your potential results.

well lets put that myth to bed first, a port throat area rarely exceeds .90% of the valves diameter., and no matter how high the valve lifts off its seat the flow can not increase too significantly much greater that the flow reached when that valve curtain area equals the port throat cross sectional area, as the smaller forms a restriction to the other.
on some heads and intake manifolds the port cross sectional area is significantly smaller than the valve curtain,
http://www.airflowresearch.com/super-chevy-apr-2010-210cc-sbc.php
EXAMPLE
this is one reason the TPI intake is rather restrictive


http://www.wallaceracing.com/chokepoint-rpm.php
heres a typical flw vs lift graph, notice how the flow rate increases past .500 lift drop rather drastically

now holding the valve open longer allows more flow just like opening a door fully allows easier access to a room but at some point just like a door opening limits the number of people that can enter a room per second so does the port throat, curtain area and any restriction in the port.
lets take your common 2.02 small block chevy intake valve, its surface area is 3.21 square inches but the port throat restriction would be exceptionally good if it was at ,90% or 2.89 square inches, a 2.02 valve has a circumference of about 6.3 inches so at about .47 inches of lift port flow increases with further lift starts to drop off
you will want to match the cam timing to the intended power range, and match the engine static compression ratio to the cam timing to get a dynamic compression ratio that will work without getting into detonation issues with available fuel octane levels.
(READ THRU THESE LINKS)
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=82
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=5078
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=796
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=727
IF YOU HAVE A SET OF REALLY DEEP POCKETS
http://www.speierracingheads.com/SRH2.50.htm
CALCULATORS
http://www.wallaceracing.com/calcafhp.php
http://www.wallaceracing.com/calchpaf.php
http://www.rbracing-rsr.com/runnertorquecalc.html
http://horsepowercalculators.net/intake ... old-design
power generated by an engine is closely linked to how efficiently it makes torque, in a given rpm range and how fast the engine can be rotated to increase the number of EFFECTIVE power strokes per second, so it should be obvious that the larger the displacement the more fuel/air mix can be burnt and the faster each cylinder can be filled and fired and scavenged and recharged the more power can potentially be produced. smaller ports will have higher flow velocity's making them more effective at filling cylinders at lower rpms but restricting upper rpm power.
larger ports tend to be far less restrictive to flow but also tend to have slower response in the lower rpm ranges
as the engines ability to efficiently fill and scavenge the cylinders is based on both port flow and time available for that port flow as the engines rpm rate increases the efficiency increases with the air flow rate inertia in the runners and ports up to the point where time limits the ability for the ports to fill, fire and scavenge efficiently, thats why you torque curve and volumetric efficiency are so closely linked.
http://www.summitracing.com/parts/tfs-3 ... /overview/
http://www.summitracing.com/parts/tfs-3 ... structions
you are aware theres reasonably priced aluminum heads designed for a small bore sbc that out flow standard vortec heads
heres a few serious sbc heads

http://www.profilerperformance.com/sbc-heads-176.html
http://www.airflowresearch.com/index.php?cPath=24_33




here’s a chart FROM THE BOOK,HOW TO BUILD BIG-INCH CHEVY SMALL BLOCKS with some common cross sectional port sizes
(measured at the smallest part of the ports)
...........................sq inches........port cc
edelbrock performer rpm ....1.43.............170
vortec......................1.66.............170
tfs195......................1.93.............195
afr 180.....................1.93.............180
afr 195.....................1.98.............195
afr 210.....................2.05.............210
dart pro 200................2.06.............200
dart pro 215................2.14.............215
brodix track 1 .............2.30.............221
dart pro 1 230..............2.40.............230
edelbrock 23 high port .....2.53.............238
edelbrock 18 deg............2.71.............266
tfs 18 deg..................2.80.............250
you don,t generally find a ports most restrictive or smallest cross section at the intake to head gasket match so measuring a port at that point is usually nearly meaningless.
notice how the port cc range does NOT exactly reflect the cross sectional areas
also notice how the 210cc AFR port is only about 4% larger in cross sectional area, a change in area that will cause about a 150rpm change in the ports low rpm torque peak , but the increased flow will have a much more significant effect on the engines power, while its true that the smaller port will make a bit more low speed torque its also true that its smaller cross section is far more restrictive to upper rpm peak hp than the slightly larger port and its the, engine displacement, compression ratio, ignition timing curve, cam timing and intake runner and plenum, header length, collector design and and exhaust back pressure, selected that have by far the larger effect on the engines power curve in the low and mid rpm ranges

you will usually need snap gauges and a micrometer to measure the port throat and the area near the push rod passage where many ports tend to be pinched tighter



there are very useful calculators to use to calculate the ideal port cross sectional area, and to use to find when a ports to small and restrictive or two large and sluggish, but it requires measuring the ports to get the correct info
http://www.rbracing-rsr.com/runnertorquecalc.html
http://www.wallaceracing.com/max-rpm2.php
http://www.wallaceracing.com/max-rpm.php
http://www.wallaceracing.com/ca-calc.php
http://www.wallaceracing.com/chokepoint-rpm.php
http://www.wallaceracing.com/area-under-curve.php
http://www.wallaceracing.com/curtain-area-calc.php
http://2.3liter.com/Calc2.htm#MinCross
related useful threads, with a ton of related info that will help in any head selection
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=333
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=796
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=148
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=2630
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=266&p=322&hilit=215cc+vortec#p322
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=4664
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=4081
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=1563
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=4221
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=401
viewtopic.php?f=52&t=92
viewtopic.php?f=55&t=1038\
viewtopic.php?f=55&t=5378
viewtopic.php?f=55&t=4362
Last edited by a moderator: