http://www.millerwelds.com/resources/ar ... rode-guide
http://store.cyberweld.com/wetuel.html
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1nLsrcsc ... re=related
http://www.millerwelds.com/products/hel ... sics5.html
http://www.airgas.com/content/details.a ... 0000000178
http://www.airgas.com/content/details.a ... 0000000141
http://www.airgas.com/content/details.a ... 0000000142
http://www.circletrack.com/howto/ctrp_0 ... index.html
http://garage.grumpysperformance.co...sten-size-amp-chart-per-metal-thickness.9235/
Select Your Stick or TIG Electrode
If you plan to weld with a particular diameter electrode, you need to know its operating range (basically, smaller electrodes carry less current, larger electrodes carry more current). The following chart suggests operating ranges for common Stick, wire, TIG and carbon arc gouging electrodes. This helps you determine which electrode sizes you can use with a particular machine.
Amperage for Stick Electrodes
Stick diameter and type 3/32" 1/8" 5/32" 3/16" 1/4"
6010, 6011 40-85 75-125 110-165 140-210 210-315
6013 40-90 80-130 105-180 150-230 250-350
7018 60-100 110-165 150-220 200-275 320-400
Amperage and Voltage for Wire Electrodes — Part 1
Wire diameter and type .030" .035" .045" .052" 1/16"
Tubular (flux or metal cored) N/A N/A 15-36V
105-340A 15-36V
105-430A 15-40V
140-480A
Self-shielded flux cored N/A 14-20V
50-120A 13-20V
80-220A N/A 14-22V
146-322A
Solid (MIG) 17-23V
50-200A 18-25V
50-225A 18-34V
85-355A 21-39V
150-500A 26-40V
250-610A
Amperage and Voltage for Wire Electrodes — Part 2
Wire diameter and type .072" 5/64" 3/32" 7/64" 1/8"
Tubular (flux or metal cored) 22-36V
200-495A 23-33V
250-510A 24-36V
355-615A N/A 26-32V
375-640A
Self-shielded flux cored 16-25V
130-350A 16-35V
200-545A 16-35V
200-525A 22-33V
310-625A 28-38V
400-600A
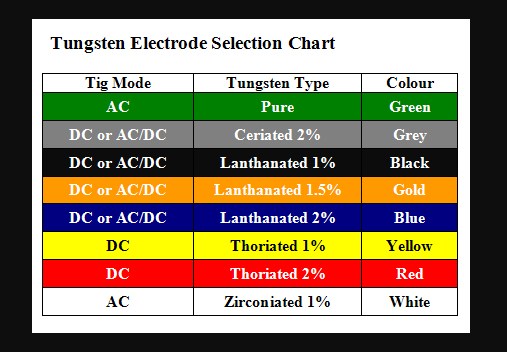
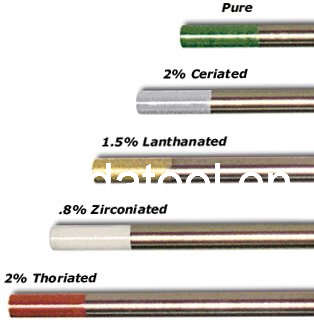
Amperage for TIG Welding
Tungsten type & diameter 1/16" 3/32" 1/8" 3/16" 1/4"
2% type 50-140 125-200 150-325 300-340 -
Pure type 60-90 125-160 190-240 260-320 330-450
Amperage for Carbon Arc Gouging
Carbon diameter 3/16" 1/4" 5/16" 3/8" 1/2"
Amperage 250 300 500 600 750
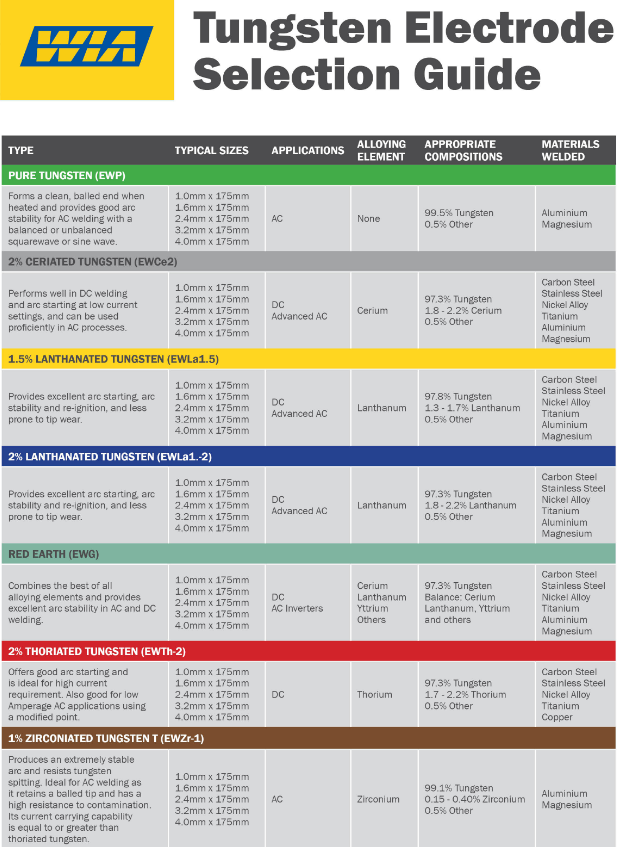
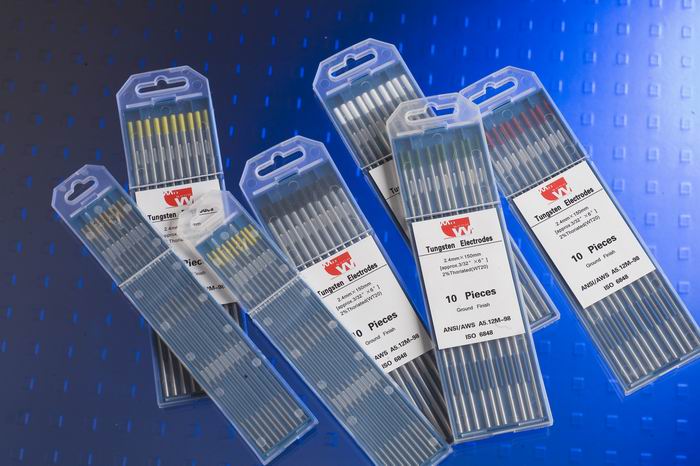
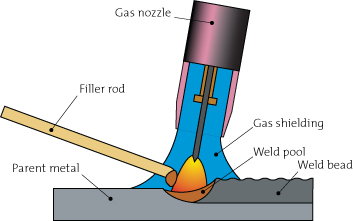
TIG welding (Tungsten Inert Gas) or Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) is frequently used for high quality, precision welding. In TIG welding, there is an arc that forms between the metal and the permanent non-melting tungsten electrode. Gas is fed through the torch, shielding the electrode and molten weld pool. If filler material is to be used, it is added separately to the weld pool.
Some of the benefits of TIG welding include superior quality welds, precise control of welding variables such as heat, freedom from splatter and low distortion. In addition, with TIG welding the process can be used at lower amperages for thinner metal and can be used on exotic metals. Some of the general drawbacks for TIG welding include the requirement for greater manual dexterity than other forms of welding, lower deposition rates and greater cost for welding thicker sections.
The commonly used power source for TIG welding is AC current. Direct current is sometimes used but due to high heat generation on the tungsten electrode and poor oxide cleaning its use is limited. Argon gas is most commonly used in TIG welding as the shielding gas. Just by changing the diameter of the tungsten electrode, welding may be performed within a wide range of heat input at different thicknesses, offering great flexibility in the process.
TIG welding can be used on many different types of metals, but is most commonly used with aluminum, especially with metals of a smaller thickness. Because of the popularity in automotive applications, TIG welding has become popular within the circles of professional racing teams along with being a favorite for auto enthusiasts and hobbyists as well.
In TIG welding, an acceptable weld is obtained only if the filler wire is clean and of high quality. If the filler wire is not clean, a large amount of contaminant may be introduced into the weld pool making for an unacceptable weld.



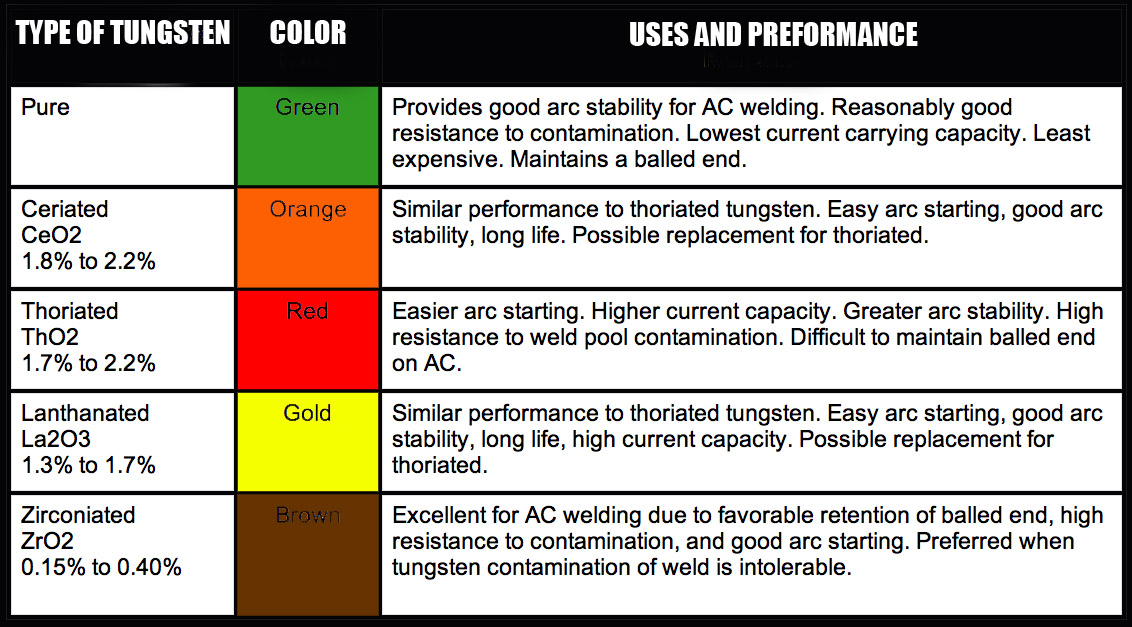

http://store.cyberweld.com/wetuel.html
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1nLsrcsc ... re=related
http://www.millerwelds.com/products/hel ... sics5.html
http://www.airgas.com/content/details.a ... 0000000178
http://www.airgas.com/content/details.a ... 0000000141
http://www.airgas.com/content/details.a ... 0000000142
http://www.circletrack.com/howto/ctrp_0 ... index.html
http://garage.grumpysperformance.co...sten-size-amp-chart-per-metal-thickness.9235/


Select Your Stick or TIG Electrode
If you plan to weld with a particular diameter electrode, you need to know its operating range (basically, smaller electrodes carry less current, larger electrodes carry more current). The following chart suggests operating ranges for common Stick, wire, TIG and carbon arc gouging electrodes. This helps you determine which electrode sizes you can use with a particular machine.
Amperage for Stick Electrodes
Stick diameter and type 3/32" 1/8" 5/32" 3/16" 1/4"
6010, 6011 40-85 75-125 110-165 140-210 210-315
6013 40-90 80-130 105-180 150-230 250-350
7018 60-100 110-165 150-220 200-275 320-400
Amperage and Voltage for Wire Electrodes — Part 1
Wire diameter and type .030" .035" .045" .052" 1/16"
Tubular (flux or metal cored) N/A N/A 15-36V
105-340A 15-36V
105-430A 15-40V
140-480A
Self-shielded flux cored N/A 14-20V
50-120A 13-20V
80-220A N/A 14-22V
146-322A
Solid (MIG) 17-23V
50-200A 18-25V
50-225A 18-34V
85-355A 21-39V
150-500A 26-40V
250-610A
Amperage and Voltage for Wire Electrodes — Part 2
Wire diameter and type .072" 5/64" 3/32" 7/64" 1/8"
Tubular (flux or metal cored) 22-36V
200-495A 23-33V
250-510A 24-36V
355-615A N/A 26-32V
375-640A
Self-shielded flux cored 16-25V
130-350A 16-35V
200-545A 16-35V
200-525A 22-33V
310-625A 28-38V
400-600A
Amperage for TIG Welding
Tungsten type & diameter 1/16" 3/32" 1/8" 3/16" 1/4"
2% type 50-140 125-200 150-325 300-340 -
Pure type 60-90 125-160 190-240 260-320 330-450
Amperage for Carbon Arc Gouging
Carbon diameter 3/16" 1/4" 5/16" 3/8" 1/2"
Amperage 250 300 500 600 750
TIG welding (Tungsten Inert Gas) or Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW) is frequently used for high quality, precision welding. In TIG welding, there is an arc that forms between the metal and the permanent non-melting tungsten electrode. Gas is fed through the torch, shielding the electrode and molten weld pool. If filler material is to be used, it is added separately to the weld pool.
Some of the benefits of TIG welding include superior quality welds, precise control of welding variables such as heat, freedom from splatter and low distortion. In addition, with TIG welding the process can be used at lower amperages for thinner metal and can be used on exotic metals. Some of the general drawbacks for TIG welding include the requirement for greater manual dexterity than other forms of welding, lower deposition rates and greater cost for welding thicker sections.
The commonly used power source for TIG welding is AC current. Direct current is sometimes used but due to high heat generation on the tungsten electrode and poor oxide cleaning its use is limited. Argon gas is most commonly used in TIG welding as the shielding gas. Just by changing the diameter of the tungsten electrode, welding may be performed within a wide range of heat input at different thicknesses, offering great flexibility in the process.
TIG welding can be used on many different types of metals, but is most commonly used with aluminum, especially with metals of a smaller thickness. Because of the popularity in automotive applications, TIG welding has become popular within the circles of professional racing teams along with being a favorite for auto enthusiasts and hobbyists as well.
In TIG welding, an acceptable weld is obtained only if the filler wire is clean and of high quality. If the filler wire is not clean, a large amount of contaminant may be introduced into the weld pool making for an unacceptable weld.






Last edited by a moderator:
